Mesothelioma, a rare cancer caused by asbestos exposure has claimed the lives of 13,000 Australians since 1980. It is expected that another 25,000 will die from the disease in the following decades. Australia has the second highest number of mesothelioma cases in the world.
Mesothelioma affects the mesothelium, a membrane that covers most of the internal organs of the body. The cancer develops years after asbestos exposure. Most often incurable unless found in its early stages where the affected area can be removed by surgery, mesothelioma is managed only to prolong life and provide the patient with as much care and comfort as possible.
What is Mesothelioma?
Mesothelioma is a cancer that develops in the mesothelium. The mesothelium is a protective sac that envelopes the internal organs of the body, it comes in many names depending on the internal organ that it protects. Due to asbestos exposure, the mesothelium in the pleura and peritoneum can develop tumors that can spread and encase the lungs.
What Causes Mesothelioma?
Asbestos exposure and mesothelioma are inseparable. Asbestos entering the body through inhalation of asbestos fibers or ingestion of asbestos-laden water are the known causes of mesothelioma.
Asbestos was an insulation material widely used in the fields of construction, carpentry, plumbing, mining, electrical engineering and shipbuilding. Also, secondary exposure of family members of workers in the industries stated above are also at risk of developing mesothelioma, thereby giving importance to asbestos disposal in Melbourne and management.
Aside from asbestos, eriolite, a zeolite mineral, with properties similar to asbestos, has also been found to cause mesothelioma. But the development of mesothelioma due to eriolite is limited to families with a genetic predisposition to develop mesothelioma. Asbestos exposure is still the leading cause of mesothelioma.
Australia has banned the use of asbestos from December 31, 2003.
Types of Mesothelioma
Mesothelioma is cancer of the mesothelium, the protective sac that covers internal organs. As already mentioned it has many names depending on its location.
For mesothelioma affecting the lungs, we name three that develop malignant cells.
● Visceral Pleura – the mesothelium surrounding the lungs.
● Parietal Pleura – the mesothelium lining the chest wall.
● Peritoneum – the mesothelium lining pelvic and abdominal cavities.
The most common mesothelioma is one that affects the pleura. When a person breathes, the visceral pleura slides against the parietal pleura, and to aid in the sliding of the pleura, it is lubricated by a slick of fluid.
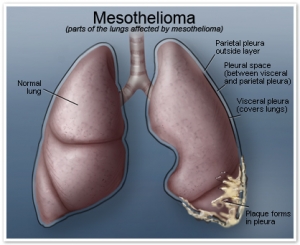
At the onset of mesothelioma, there is an excess production of the fluid made by the pleura and this creates pressure on the lung. This is called pleural effusion. Mesothelioma normally starts in one lung, but as the disease progresses while the tumor grows and scatters, the other lung ends up getting infected as well until the whole lung is encased.
How mesothelioma develops in the peritoneum is still not very clear, but it some studies show that broken pipes that carry drinking water insulated with asbestos is a path for asbestos to be ingested by the body. The asbestos is absorbed by the gut and eventually deposits in the peritoneum, thereby causing mesothelioma.
Australian Cases of Mesothelioma
Second only to the United Kingdom, Australia is one of the countries that has a high number of mesothelioma cases. The number of people reporting symptoms of mesothelioma ended up reaching 600 new cases of mesothelioma in 2007. 84% of the cases reported were men with a range between 75 to 79 years of age. Reported deaths reached 551 for the same year. By 2011, people who reported mesothelioma symptoms reached nearly 131 new confirmed diagnoses.
A survey of the trend of mesothelioma cases indicate that the number will go up with a peak in deaths between 2014 and 2021. According to the Australian Institute of Health and Welfare, the number of mesothelioma cases will reach 18,000. The demographic of mesothelioma deaths consist 70% of both men and women over 65 years of age.
Symptoms
Mesothelioma takes time to develop, not until the disease has considerably progressed to advanced stages will mesothelioma symptoms present themselves. Mesothelioma is a type of cancer that is difficult to diagnose as early symptoms of mesothelioma will be mistaken for common, everyday ailments.
From the time of initial exposure to the time symptoms of mesothelioma can conclusively be diagnosed, it can take between 20 to 50 years. Of the two types of mesothelioma affecting the lungs, only pleural mesothelioma is categorized into stages.
Pleural Mesothelioma Symptoms
When the visceral and parietal mesothelium develop tumors due to asbestos exposure, the asbestos fibers find their way through the trachea or bronchi and eventually penetrate the pleural lining. The asbestos fibers which are categorized as cancer-causing, damage the DNA of the mesothelium, causing unprecedented cell growth leading to mesothelioma.
Stage 1.
Sub-Stage 1a. In this stage, the tumors are so small and so localized that no symptoms are hardly felt by the patient. In this stage where the tumors are in a scattered pattern, it is called diffuse mesothelioma. The tumors can either be in the visceral or in the parietal pleura, the pleura lining the chest wall.
Sub-Stage 1b. Diffuse mesothelioma is now found within the inner layer, the visceral pleura. At this stage, pleural effusions can be observed. Very generic symptoms for mesothelioma can range from fever, chest pain, body aches and coughing.
Stage 2.
At stage 2 of the mesothelioma some localized small tumors can be found within the chest, but may start to spread from the pleura to other parts of the lung and may also spread to the diaphragm. Aside from the pleural effusion, the patient may now develop pleural thickening. This is due to the scarring from the asbestos exposure and due to the tumor growth. The patient may then experience dyspnea or difficulty breathing. Some symptomatic weightless may also be reported by the patient.
Stage 3.
This is the stage where majority of patients are diagnosed. Stage 3 is marked by the increase in severity of the mesothelioma symptoms described at Stage 2. In addition to this, many stage 3 symptoms are very similar to patients suffering from lung infections like bronchitis and pneumonia. At this stage, the tumors have spread throughout the pleura and chest cavity on one side of the body.
Tumors may also be found in the lymph nodes, pericardium (lining of the heart) and diaphragm, the chest wall and other adjacent tissue. Depending on how the tumors have metastasized, mesothelioma symptoms will include chest paint or tightness and shortness or difficulty breathing. Fever, fatigue and weight loss are other symptoms as well.
Stage 4.
Stage 4 is the most advanced stage where the cancer has spread throughout the chest cavity and often to other internal organs and tissues on both sides of the body. List of symptoms include night sweats, fever, chest pain and tightness, shortness of breath, fatigue and weight loss. Other symptoms include, anemia, hemoptysis (coughing up blood), fluid buildup, and dysphagia (difficulty swallowing).
Peritoneal Mesothelioma Symptoms
This cancer affects the peritoneal mesothelium, the protective sac in the abdomen. Like peritoneal mesothelioma, peritoneal mesothelioma is also hard to diagnose due to a lack of distinct symptoms. Similar to how asbestos in lodged in the lungs, asbestos fibers can be coughed up, swallowed and deposit themselves in the stomach.
Peritoneal mesothelioma has symptoms specific to the abdomen. A list of symptoms will include abdominal distension without pain, weight loss, vomiting and nausea. Localized pain relating to the tumor is also reported. A peritoneal effusion, fluid build up in the abdomen, may also be part of the mesothelioma symptoms. Painful bowel obstructions are also ordinary.
Who’s at Risk?
Australians who have spent time in the following trades are at risk of being afflicted with mesothelioma:
● Construction
● Carpentry
● Plumbing
● Electrical Engineering
● Insulation workers
● Pipe fitters
● Shipbuilding and repair
● Automotive manufacture and repair
It is important to note that a study in the UK and Australia post carpenters and construction workers are at a particularly high risk of developing mesothelioma due to asbestos exposure. This came from a survey of 600 patients where the study showed that 1 out of 10 carpenters born before 1950 would die of mesothelioma.
Diagnosing Mesothelioma
Diagnosing mesothelioma can is difficult because of the many common symptoms of common pulmonary afflictions. It is usually detected after undergoing an imaging test but can only be confirmed after a biopsy. It should be differentiated with other pulmonary malignancies including primary lung carcinoma, reactive pleural disease, other metastasized cancers reaching the pleura and other primary pleural cancers.
Administered by a qualified medical professional, routine tests in the hospital will include checking the patient’s medical history, where a thorough evaluation of mesothelioma risk factors will be assessed if the patient exhibits symptoms of mesothelioma.
One of the key questions the medical professional will ask is if the patient has had asbestos exposure in the past. Tests such as physical examinations, blood tests, imaging tests such as x-rays, CT or CAT scans and MRI’s are helpful diagnostic tools to validate a suspected mesothelioma cases. A biopsy confirms a suspected mesothelioma.
Imaging Tests
Prior to any test, a review of the medical history of the patient is done to aid in diagnosis. Qualifying questions will be asked such as a history of asbestos exposure, if the patient indeed has a history of asbestos exposure, this will raise and increase the suspicion of mesothelioma. After a physical exam, an x-ray may follow then a lung function test. The presence of pleural thickening in the x-ray images will further increase the suspicion of mesothelioma. Further imaging tests such as an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) or a CT scan will be performed to strengthen the suspicion.
Biopsy
A biopsy confirms a mesothelioma diagnosis. A tissue sample is taken from the patient and examined under a microscope by a pathologist.
The biopsy can be done in different ways depending where the malignancies are detected.
Thoracoscopy – For determining cancers found in the chest. It is done by placing a thin, lighted tube called a thoracoscope into the chest through an incision between two ribs. It allows the doctor to look inside the chest and take the necessary sample.
Thoracotomy – This procedure opens up the chest directly to view and take a sample.
Laparoscopy – This procedure allows the doctor to see into the abdominal cavity and obtain tissue for examination through a small incision by placing a laparoscope into the incision. It is considered to be a less invasive procedure.
If these diagnostic surgeries do not yield substantial samples and a diagnosis cannot be performed, a more extensive surgery must be carried out.
Immunochemistry
To validate a mesothelioma diagnosis, we turn to immunochemistry.
Immunochemistry is the study of molecular mechanisms that underlie the functions of the immune system, looking at the nature of antibodies, antigens and their interactions.
This branch of chemistry aids the pathologist in differentiating malignant mesothelioma from, say, neoplastic mimics. This is to differentiate whether the cancer that has affected the pleura is not the same cancer that has affected the breast or lung that has only metastasized into the pleura. The pathologist look for ‘markers’ that differentiate mesothelioma from other cancers. Though there are tests and panels available, no single test is perfect to make a singular diagnosis.
Example of Immunohistochemistry Results:
Positive:
EMA (epithelial membrane antigen) in a membranous distribution
WT1 (Wilms’ tumour 1)
Calretinin
Mesothelin
Cytokeeratin
HBME-1 (human mesothelial cell 1)
Podoplanin (PDPN)
Osteopontin
Negative:
CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen)
B72.3
MOC-3.1
CD15
Ber-EP4
TTF-1 (thyroid transcripton factor-1)
Claudin-4
Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM)
Estrogen receptor beta
Mammaglobin
The appropriate treatment to administer for people suffering from mesothelioma depends on the severity (stage) of the disease when diagnosed taking into consideration the preference of the patient.
Mesothelioma Treatment
Treatment options will include the following:
1. Pleurectomy. This is removal of the affected tissue by surgery. Pneumonectomy is the removal of the whole affected lung while lobectomy is the surgical removal of part of the affected lung. Surgery is only applicable if tumours are found small.
2. Phototherapy. Usually done during a pleurectomy, stray cancer cells are treted with a special dye that will highlight the tumors to aid in seeing the stray tumors, the tumors are then killed with a laser.
3. Thoracentesis. Done by inserting a needle in between the ribs to draw off the built up fluid (pleural effusion) out of the cavity.
4. Pleurodesis. Done by inserting an endoscope (a special slender instrument) to inject a special powder in between the pleural layers. This causes the pleural layers to get inflamed arresting the production of excess fluid.
5. Paracentesis. Similar to thoracentesis, except the needle is inserted into the peritoneal cavity to remove excess fluid.
6. Peritoneal Surgery. This is done to remove tumors in the abdominal cavity.
7. Chemotherapy. Uses cancer-killing drugs that can shrink the cancer, thus, relieving mesothelioma symptoms. Chemotherapy is used when other treatments have failed or the cancer has relapsed.
8. Radiotherapy. Uses x-rays to kill cancer cells. This procedure can only be used on small areas for fear of killing nearby healthy cells. Used to ease pain and breathlessness.
9. Complementary and alternative therapies. These treatments are used alongside the patient’s primary cancer treatment of choice to improve quality of life.
All treatments causes side effects, to pick the best one, the patient is recommended to talk to the doctor to discuss the best treatment available. The effects of the treatment may be temporary, others may be permanent. Again, it is best to discuss all alternatives before foregoing one.
Mesothelioma Research
Mesothelioma research is ongoing. Clinical trials are being carried out either to test promising new treatment methods or combinations of existing cancer treatments. Consider these options with your doctor.
Mesothelioma Patient Care
Providing care for mesothelioma patients can be difficult. Emotionally draining, taking the high road and looking after mesothelioma patients needs and providing comfort should be a priority. Finding help, a support group and informative reading materials may help in easing uncertainties, fears and doubts.
Falling into disease and undergoing treatment may make a patient differently about one’s body. The patient may see one’s body differently, see one’s person differently and the different relationships surrounding the patient. It may affect the patient’s sexuality. These changes can ultimately be upsetting.
It is key that the patient remain open to the people around here to dispel doubts and fears.
Getting Help in Australia
The growing number of patients exhibiting mesothelioma symptoms prompted the Australian government put place importance on offering quality treatment. Below is a list of institutions offering treatment for mesothelioma:
Bernie Banton Centre at Concord Hospital. Situated in Sydney, NSW, it is home to the Asbestos Disease Research Institute. It is the world’s first stand-alone research facility catering to the prevention and treatment of asbestos-related diseases.
Austin Health Centre. Situated in Melbourne, Victoria, it is home to Dr. Malcol Feigen, a pioneer in his field for new radiotherapy techniques by using high-dose radiation is successful in adding an average of two years to the survival rate of patients involved in the program.
Sir Charles Gairdner Hospital. Situated in Perth, Western Australia it is the only designated comprehensive cancer treatment center in Western Australia. It is a large teaching hospital catering to innovative experimental immunotherapy treatments for mesothelioma. The medical impressive staff handling mesothelioma cases compose of oncologists and thoracic surgeons.
Peter McCallum Cancer Centre. Situated in Melbourne, Victoria, this is the only public hospital dedicated to research, education and treatment of mesothelioma. It boasts of the largest cancer research group in the country.
Assistance for families and patients of mesothelioma is available through the Mesothelioma Center’s Patient Advocates. There is a $35 billion dollar Mesothelioma Trust Funds allotted for people affected by asbestos and mesothelioma. Patients can also take advantage of grants to cover travel, housing and treatment expenditures.